网络安全:打击猖狂犯罪份子
The balance of potentially huge financial gain versus relatively low operational risk makes cybercrime a very tempting proposition. To bring cybercrime under control the ‘good guys’ have to learn how to counter these new cyber-weapons, as well as how to build powerful weapons and protection tools of their own.
Cybercrime is the inevitable flip side of the ‘Third Industrial Revolution’, the Digital Revolution.
Cybercrime is causing massive disruption and financial damage to individuals, businesses and governments.
Cybercriminals operate in a borderless world and their activities often leave very little, if any, physical evidence.
A strategic approach to mitigating cybercrime risks is required. Finance professionals can play a leading part by:
· defining risk management strategies
· estimating the financial impact of different type of cybersecurity breaches. This enables businesses to plan how to respond
· establishing priorities for valuable digital resources to implement a layered approach to security
· remaining up-to-date with legislation and the work of regulators to ensure adequate disclosure and prompt investigation of breaches
· maintaining client confidence: A key risk for accountancy practices is the lateral movement approach where breaching one system is a stepping stone for subsequent attacks on the victim’s clients.
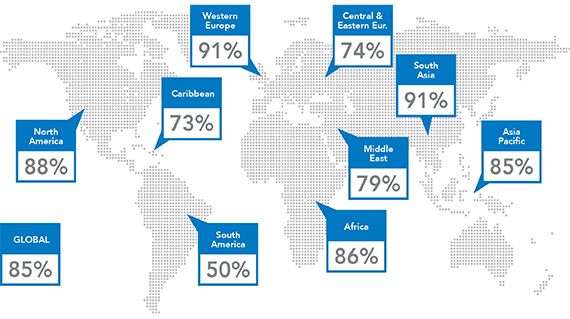
Map showing concern about cybersecurity by region. Western Europe and South Asia are the most concerned.
Into the future
Emerging technologies are playing an important part in shaping the cybersecurity landscape.
The ubiquity of mobile devices means IT departments cannot contain valuable data and hardware with a rigid perimeter that is easy to monitor and protect.
Mobile and contactless payments systems are attractive to criminals. One such system ApplePay is likely to be actively targeted.
Cloud data breaches will remain a concern. To mitigate the risks the following are being developed:
· advisory and regulatory frameworks
· methodologies for due diligence checks and
· testing of performance and resilience.
Big data - risks include ‘salami slicing’ techniques bringing together seemingly disparate data to from a pattern for use in identity fraud.
The Internet of Things (IoT) could provide detailed data of those living in a smart home, especially if poorly conceived hardware and software provides a gateway for hackers.

手机扫描二维码,关注ACCA中国官方微信。在对话框输入“0004”,即可将报告直接下载到您的手机。